When Should an Oil Immersed Distribution Transformer Be Selected?
-
When an oil immersed distribution transformer should be selected, focusing on capacity range, usage scenarios, and grid role.
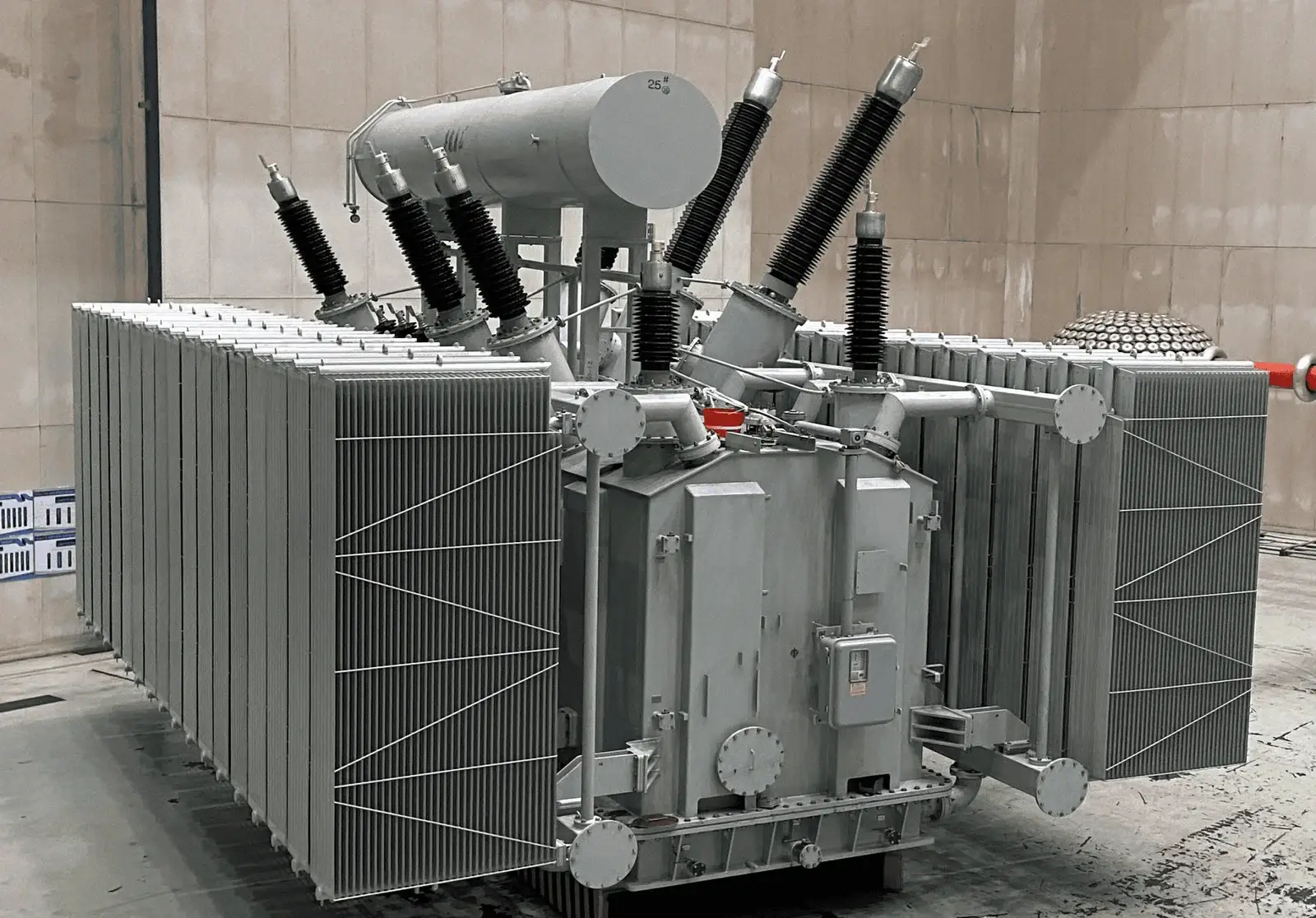
Why Distribution-Level Transformer Selection Impacts Network Performance
Distribution networks connect transmission systems with end users. This stage handles voltage reduction and local load delivery. Equipment choice affects stability and operating cost. An oil immersed distribution transformer suits specific conditions. Selection depends on capacity, environment, and duty cycle. Unlike transmission units, distribution transformers face frequent load variation. Proper selection improves efficiency and service continuity. Engineers prioritize reliability at this level. Oil immersion offers advantages under demanding conditions.
What Is an Oil Immersed Distribution Transformer?
An oil immersed distribution transformer reduces voltage for end-use applications. Insulating oil surrounds windings and core. Oil provides cooling and electrical insulation. These transformers operate below transmission voltage levels. Typical installations include substations and outdoor enclosures. Compared with dry units, oil immersed designs handle higher thermal stress. Distribution-focused models emphasize continuous operation and load adaptability. Their structure supports frequent switching and variable demand.
How Distribution Transformers Differ from Power Transformers
Power transformers operate within transmission networks. Distribution transformers serve downstream loads. Voltage levels differ significantly. Capacity ranges remain lower for distribution units. Load profiles also vary. Distribution transformers experience daily fluctuations. Power transformers handle steady bulk transfer. Oil immersed power distribution transformer designs balance efficiency and durability. This distinction guides correct equipment placement within the grid.
Typical Capacity Ranges for Oil Immersed Distribution Transformers
Capacity selection defines performance and lifespan. Undersized units overheat under peak load. Oversized units waste capital and efficiency. Oil immersed distribution transformers cover a wide range.
-
50 kVA to 500 kVA for residential areas
-
500 kVA to 2500 kVA for commercial zones
-
2500 kVA to 10000 kVA for industrial distribution
Why Capacity Matching Matters in Distribution Systems
Load diversity shapes distribution demand. Residential loads peak during evenings. Commercial zones peak during business hours. Industrial loads remain continuous. Proper capacity matching prevents thermal overload. Oil immersion stabilizes temperature under variable load. Correct sizing extends service life. Utilities rely on accurate load forecasting for transformer selection.
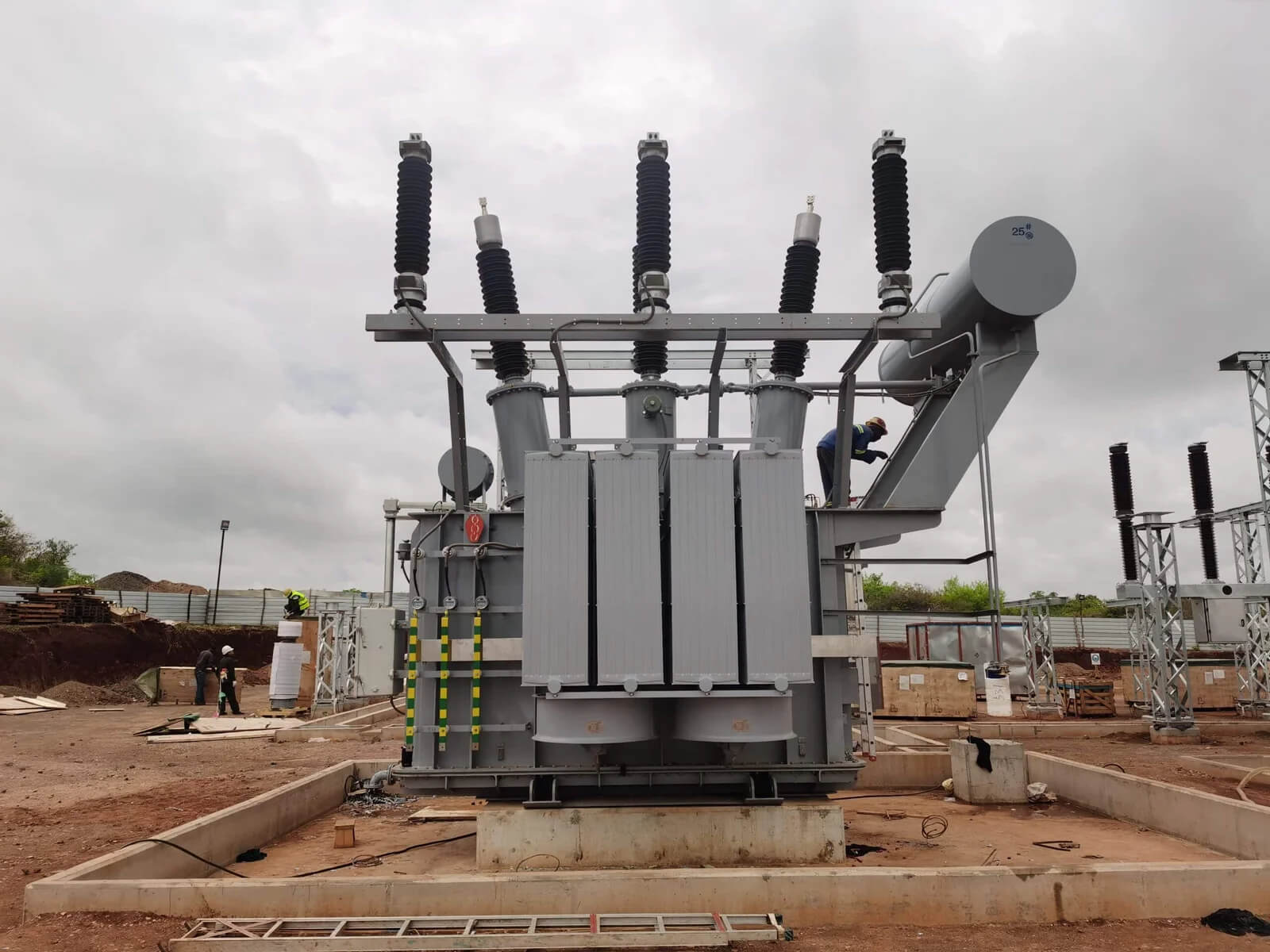

Common Voltage Levels in Distribution Applications
Distribution voltage varies by region and application. Oil immersed designs adapt to these standards.
| Application | Primary Voltage | Secondary Voltage | Typical Capacity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Residential | 10 kV / 11 kV | 400 V | 100–500 kVA |
| Commercial | 11 kV / 20 kV | 400 V | 500–2500 kVA |
| Industrial | 20 kV / 35 kV | 690 V | 2500–10000 kVA |
How Voltage Levels Influence Transformer Selection
Primary voltage determines insulation requirements. Secondary voltage defines end-user compatibility. Oil immersion supports higher insulation margins. Voltage variation affects cooling demand. Distribution planners select transformers based on grid standards. Proper alignment ensures safety and efficiency.
When Oil Immersion Becomes the Preferred Choice
Oil immersed distribution transformers excel under certain conditions.
-
Outdoor installations with limited enclosure protection
-
High ambient temperature regions
-
Continuous or fluctuating load profiles
-
Medium to high capacity requirements
Why These Conditions Favor Oil Immersed Designs
Outdoor environments expose equipment to heat and moisture. Oil insulation tolerates these stresses. High temperatures challenge air-cooled systems. Oil transfers heat more effectively. Load fluctuation increases thermal cycling. Oil damping reduces mechanical stress. These factors justify oil immersion in many distribution scenarios.
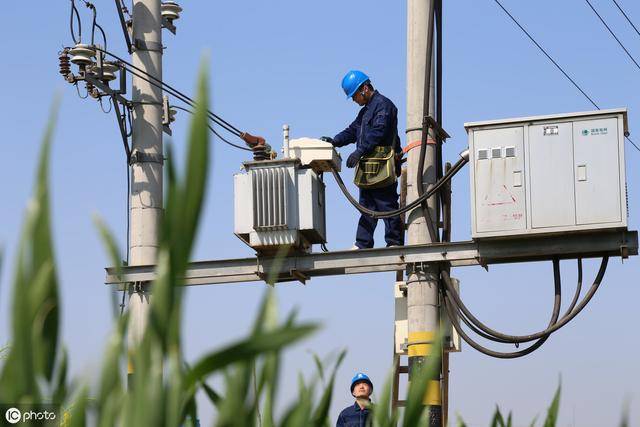

Typical Use Scenarios for Oil Immersed Power Distribution Transformers
Urban substations rely on compact reliability. Industrial parks demand robust energy supply. Rural networks require durable equipment. Renewable integration adds variability. Oil immersed transformers adapt well to these demands. Their sealed design resists contamination. Maintenance intervals remain manageable. Utilities value this flexibility across diverse environments.
How Distribution Transformers Support Grid Stability
Distribution transformers stabilize voltage near consumption points. Oil immersion maintains consistent winding temperature. Stable temperature preserves impedance balance. Balanced impedance ensures steady voltage output. This stability protects downstream equipment. Sensitive loads benefit from reduced fluctuation. Distribution-level reliability strengthens the entire grid.

Relationship Between Distribution and Power Transformers
Distribution transformers form the final stage of voltage reduction. Power transformers supply them from transmission networks. Both categories complement each other. Oil immersed designs appear in both roles. However, specifications differ. Distribution models focus on adaptability. Power transformers emphasize bulk transfer. Understanding this relationship avoids misapplication. For upstream context, reference the Power Transformer category.
Maintenance Considerations for Distribution Transformers
Oil immersed distribution transformers require periodic inspection. Oil quality monitoring prevents insulation degradation. Sealing integrity ensures moisture resistance. Cooling efficiency depends on oil circulation. Routine checks extend operational life. Compared to dry units, oil systems demand structured maintenance. Utilities plan service schedules accordingly.
When Should an Oil Immersed Distribution Transformer Be Selected?
Oil immersed distribution transformers suit demanding distribution environments. Capacity range flexibility supports diverse loads. Oil insulation improves thermal stability. Outdoor and industrial settings benefit most. Correct selection enhances efficiency and reliability. These transformers bridge transmission and end-use systems effectively. Their role within the broader Power Transformer framework remains essential.
FAQ
When is an oil immersed distribution transformer better than a dry type unit?
Oil immersed distribution transformers perform better under higher thermal stress. Outdoor installations benefit from oil insulation. High load fluctuation favors oil cooling. Dry units suit indoor environments with lower capacity. Selection depends on environment, load profile, and maintenance strategy. Utilities often prefer oil immersed designs for outdoor substations.
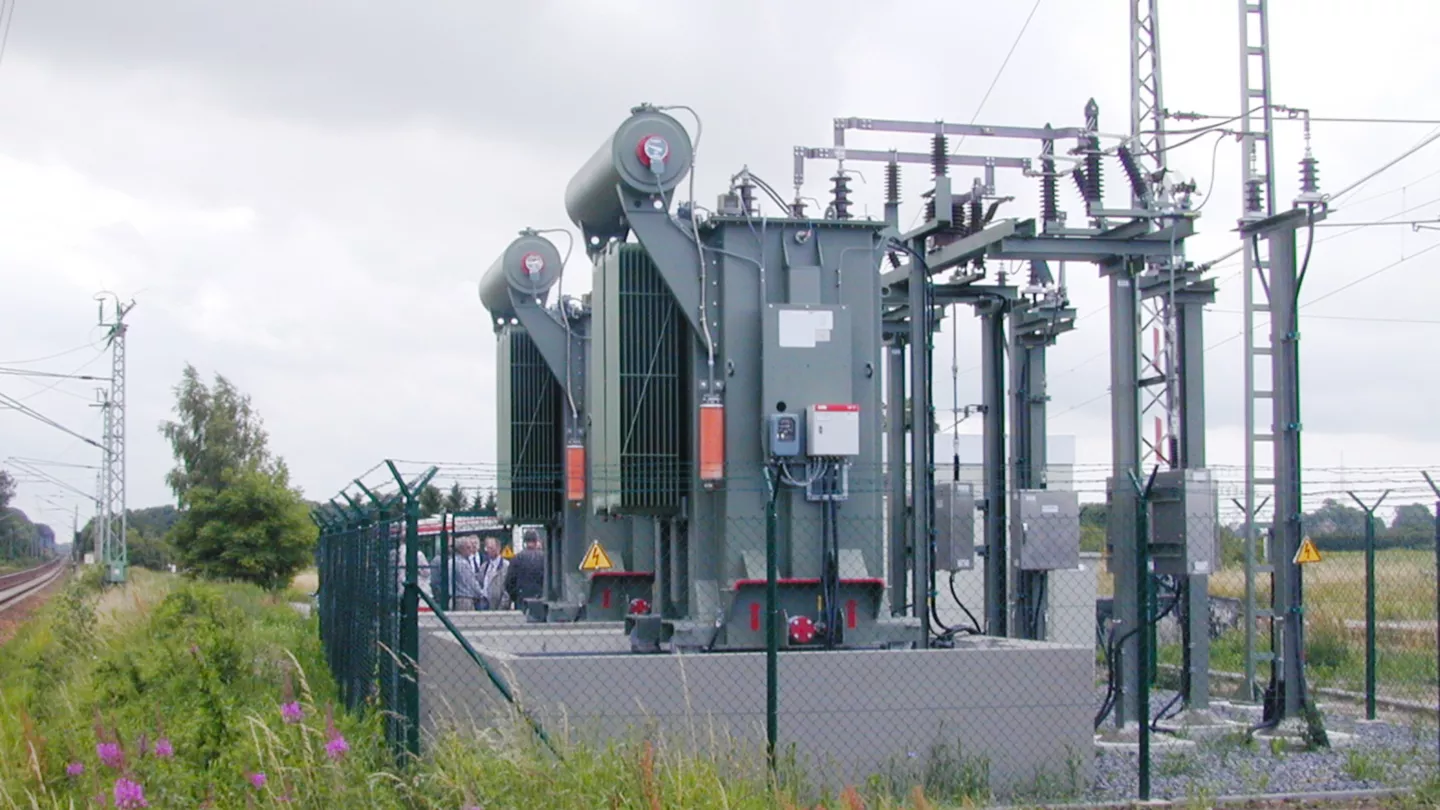

What capacity range defines a distribution transformer?
Distribution transformers typically operate below transmission ratings. Common capacities range from 50 kVA to 10000 kVA. Residential areas use smaller units. Industrial facilities require higher ratings. Oil immersion supports this wide range. Proper sizing ensures efficiency and longevity.
How does a distribution transformer differ from a power transformer?
Distribution transformers serve end users directly. Power transformers operate within transmission networks. Voltage levels and load profiles differ. Distribution units handle frequent variation. Power transformers manage steady bulk transfer. Both types complement each other within grid architecture.
